Banking in Kenya dates back to the pre-colonial periods. The first banks largely concentrated on financing international trade along the Europe-South Africa–India axis, but later diversified operations to tap the opportunities for profitable banking created by a growing farming settler community and pioneer traders in the local economy to whom they provided deposit and credit facilities.
Indian money lenders operating quasi bank services as early as the 18th century were probably the first bankers but the first recognisable bank was Jetha Lila Bankers from India, which was established in Zanzibar in 1880. In 1889 the National Bank of India appointed the trade house of Smith Mackenzie to be their agent in Zanzibar. Smith Mackenzie had a Mombasa branch in 1887 which was taken over by the Imperial British East Africa (IBEA) in 1888. The National Bank of India established its own office in Zanzibar in 1892. In July 1896 the National Bank of India established a branch in Mombasa renting premises from Sheriff Jaffer.
In April 1909, the East Africa Post Office Savings Bank Ordinance was passed and in April of the following year, the Ordinance for the Regulation of Banks established in the East Africa Protectorate was passed. The former Ordinance established the first bank in the formal sense while the latter enabled the National Bank of India to become the first commercial bank. By 1911 there were only three banks: The National Bank of India, The Standard Bank of South Africa that came in December 1910 which later merged with Anglo-Egyptian Bank Ltd to form Barclays Bank in 1926 and Kathiawad and Ahmedabad Banking Corporation which had a short-lived presence in Mombasa from 1910 to 1915.
In 1920 the East Africa Protectorate was declared a colony of the British Empire and its name changed to Kenya. The new colonial starters helped the Banks grow rapidly mainly through European Deposits and Asian customers. The banking services were not available to Africans, the only banking sources for Africans was the Post Office savings bank which started in 1910 as a department of the Colonial Postal service, even then the service was only available in places where Officials of the colonial service were stationed and therefore did not reach the majority of Africans who resided in rural areas.
The steadily growing economy in Kenya would soon lead to an influx of new banks between 1950 and 1959. In 1951 the Dutch bank Nedelandsche opened a branch in Nairobi. It was followed by the Bank of India which opened its first branch in Treasury square in Mombasa on January 17th 1953 and the Bank of Baroda on December 4th of the same year with its first branch also in Mombasa. The Pakistan based Habib Bank AG Zurich Ltd came in 1956 while the Ottoman Bank and Commercial Bank of Africa (CBA) rounded off the rush by establishing branches in the country in 1958.
After Indian attaining independence from Britain in 1947 and the subsequent hiving off of Pakistan, India changed its name in 1958 to National Oversees and Grindlays bank later called National and Grindlays Bank following its merger with Grindlays bank another landing based bank which traced its roots to Calcutta India. By 1951 the Banks had expanded its branches considerably but employment opportunities for Africans in the Banking industry took a long time to materialize. Indeed, it was not until June 1963 a few months before the country attained independence that the first African manager of a Bank branch Peter Nyakiamo was appointed.
After independence, the changing landscape of banking began to note the entrance of fully indigenous banks. In June 1965 the first fully locally owned Commercial Bank, the Cooperative Bank of Kenya was registered as a Cooperative Society; initially, it served the growing farming community. Cooperative bank as it came to be known commenced its operations as a Bank on January 10th 1968. The first fully Government-owned Bank the National Bank of Kenya was established on June 19th 1968. In 1971, the Kenya Commercial Bank was formed following the merger of the National and Grindlays Bank, with the government owning a 60-per cent majority stake. It took the poll position as the largest of the country’s commercial banks in terms of deposits and number of branches.
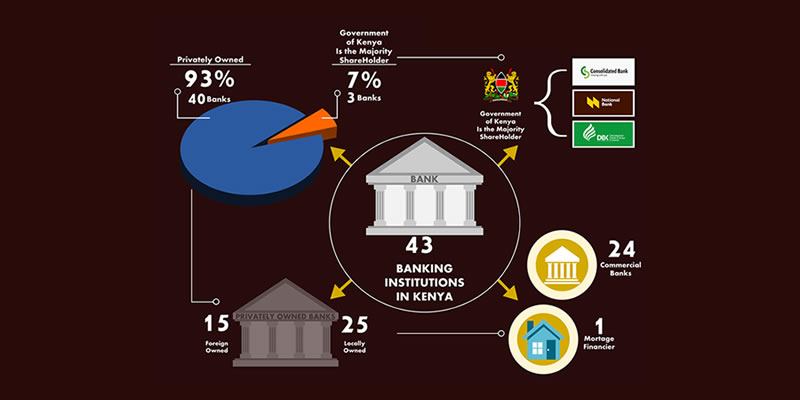
The formation of the Government-owned Banks had the desire to fight the speeding of the provision of affordable banking services to the majority of the population. It also prompted Foreign-owned bank to take measures to remain relevant in the Kenyan markets and beyond. Today, according to the Bank supervision annual report 2017, Kenya currently has 44 banks. 31 of the banks are locally owned while the remaining 13 are foreign-owned. Among the 31 locally owned banks, the government of Kenya has a shareholding in three of them, 27 of them are commercial banks and one is a mortgage finance institution, known as Housing Finance.

Of the 44 banks, ten are listed on the Nairobi Securities Exchange with respect to the names of their shareholders namely Barclays Bank of Kenya Ltd, Stanbic Bank Kenya Limited, Equity Bank Ltd, Housing Finance Ltd, Kenya Commercial Bank Ltd, NIC Bank Ltd, Standard Chartered Bank (K) Ltd, Diamond Trust Bank Kenya Ltd, National Bank of Kenya and Co-operative Bank of Kenya Ltd. The shareholding structure of these banks constitutes, one that is state-owned, six locally owned and three that are foreign-owned.
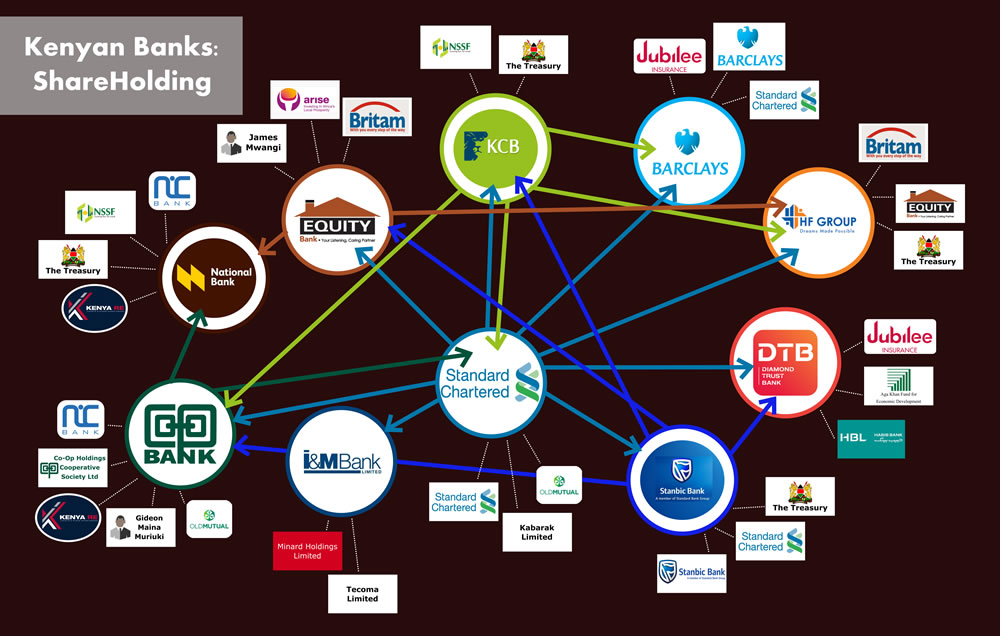
Together, they act as representatives of local, foreign, state, single and block shareholding in Kenya.
In 2016, in the wake of the collapse of three lenders —Dubai, Imperial and Chase banks — precipitated by weak corporate governance practices that allowed irregular issuing of loans to politically connected customers, wanton insider lending and running of parallel banks, the Central Bank of Kenya issued orders for banks to disclose top shareholders on their websites. An outcome of this has been greater transparency and public trust. However, as this analysis illustrates, is a network of individuals, companies and banks who are the major shareholders of Kenyan banks.
Let us examine this?
The National Bank of Kenya’s two key shareholders are the National Treasury of Kenya and the National Social Security Fund (NSSF). The NSSF holds 48.1% of the ordinary shares as well as 20.7% (253 million) of the non-cumulative preference shares in the Bank. The National Treasury holds 22.5% of the ordinary shares as well as 79.3% (900 million shares) of the Bank’s non-cumulative preference shares. The remaining 29.5% of the ordinary shares are held by the general public through the NSE namely, Kenya Reinsurance Corporations, Best Investments Decisions Ltd, Co-op bank custody a/c 4003a, Craysell Investments Limited, NIC Custodial Services a/c 077, Equity nominee Ltd a/c 00084, NBK Client a/c 1( Anonymous) and Eng. Ephraim Mwangi Maina who has 0.3% shares.
*******
Co-operative Bank of Kenya public and was listed on December 22nd 2008.
Shares previously held by the 3,805 Co-operative Societies and unions were ring-fenced under Co-op Holdings Co-operative Society Ltd which became a strategic investor in the Bank with a 64.56% stake (3 Billion shares), followed by Gideon Maina Muriuki with 1.9% shares, Kenya Commercial Bank nominees a/c 915B 0.8% shares, NIC Custodial Services a/c 077 0.7% shares,Stanbic Nominees Ltd a/c Nr 1030682 0.5% ,Aunali Fidahussein Rajabali and Sajjad Fidahussein Rajabali 0.4%, Amarjeet Balooobhai Patel and Baloobhai Chhotabhai Patel, Old Mutual Life Assurance Company,Kenya Reinsurance Corporations and Standard Chartered Nominees Resd a/c ke11443 hold 0.3% shares each.
Co-op bank custody a/c 4003a (anonymous) has shares in two banks, National Bank of Kenya and Standard Chartered.
********
On 31st December 2014, Equity Group holdings PLC finalized an internal restructuring that culminated in its conversion into a non-operating holding company, Equity Group Holdings Limited (EGHL) in order to further meet its objectives. The Bank arm was founded in 1984 as Equity Building Society (EBS). In 2006, the Bank was listed at the Nairobi Securities Exchange where it has become the largest Bank by market capitalization. The listing also attracted Helios, a strategic investor, to invest USD 185 million in 2007.
Arise BV is the top investor at Equity Bank Limited with 12% shares. Aris-constituting Norfund, FMO and Rabobank-paid kes17.6 billion for a share of Equity Group Holdings KES147 billion market valuation. Aris took over the shares held by Norfininvest.
Other shareholders include James Mwangi and British American Investment Company Kenya Ltd with 127 Million shares, Standard Chartered Nominees with 121 Million shares, Equity Bank ESOP 117 Million shares, Standard Chartered Kenya Nominees Ltd a/c 107 Million Shares, Fortress Highlands Ltd 101 Million shares, Equity nominees Ltd a/c 93 Million shares, Stanbic Nominees Ltd a/c and Aib Nominee a/c Solidus Holdings Ltd hold 92Million shares.
******
Kenya Commercial Bank, Eastern Africa is the oldest and largest commercial bank started its operations in Zanzibar as a branch of National Bank of India In 1896. The bank extended its operation to Nairobi in 1902, which had become the headquarters of the expanding railway line to Uganda. In 1975, The Government of Kenya acquired majority shareholding and changed the name to Kenya Commercial Bank. In 1988, the Government sold 20%of its shares at NSE through an IPO that saw 120,000 new shareholders acquire the bank. The National Treasury is the top investor at Kenya Commercial Bank with 17.5% shares, followed by National Social Security Fund (NSSF) with 173 Million shares, Standard Chartered Nominee a/c with 69 Million shares, Standard Chartered Nominees Ltd a/c with 63 Million shares,CFC Stanbic Nominees Ltd a/c with 61 Million shares, Standard Chartered Kenya Nominee a/c with 58 Million shares, Standard Chartered Kenya Nominees Ltd a/c with 52 Million shares ,Standard Chartered nominees a/c ke002382 with 46 Million shares, Standard Chartered nominees a/c ke9688 with 45 Million shares and Standard Chartered Kenya nominees non-resd a/c 9069 with 36 Million shares.
********
Amalgamated Banks of South Africa (ABSA) Group Limited formerly known as Barclays Africa Group Ltd has the highest shares, 68.5% at Barclays Bank of Kenya, followed by Standard Chartered Nominees Resd a/c ke8723 e with 75 Million shares, Standard Chartered nominees resd a/c ke11401 with 46 Million shares, Kenya Commercial Bank Nominees Limited a/c 915b with 41 Million shares,Standard Chartered nominees resd a/c ke11450 with 38 Million shares, Kenya Commercial Bank Nominees Limited a/c 915a with 34 Million shares, Standard Chartered nominees a/c 9230 and Standard Chartered nominees non-resd. a/c 9913 hold 23 Million shares, Goodwill (Nairobi) Limited a/c 94 with 21 Million shares and the Jubilee Insurance Company of Kenya Limited with 20 Million shares.
******
Standard Chartered Bank Kenya Limited was established in 1911 with the first branch opened in Mombasa Treasury Square. The Bank was listed on the Nairobi Securities Exchange in 1989. The public shareholding is just over 25% (remainder held by Standard Chartered PLC) and comprises over 30,000 shareholders. Standard Chartered Holdings is the top shareholder with 73.5% shares and operates as a subsidiary of Standard Chartered Holdings International B.V. Standard Chartered Holdings (Africa) BV is an Overseas UK company opened on 17 May 2002. Kabarak Limited follows with 3.5 Million shares, Co-op Bank Custody a/c 4003A with 1.9 Million shares , Standard Chartered Kenya Nominees – a/c KE002382 and Standard Chartered Nominees – resd a/c KE11450 they both hold 1.7 Million shares, Standard Chartered Nominees – a/c 9230 they both hold 1.5 Million shares, Kenya Commercial Bank Nominees Limited – a/c 915B and Standard Chartered Africa Limited, they both hold 1.4 Million shares, Old Mutual Life Assurance Company Limited with 1.3Million shares and Standard Chartered Nominees – resd a/c KE11401 holds 1.1Million shares.
Standard Chartered Kenya Nominees Ltd a/c (anonymous) has almost equal shares in two banks, Equity Bank limited and Kenya Commercial Bank.
Standard Chartered nominees a/c ke002382 (anonymous) has shares in two banks, Diamond Trust Bank and Kenya Commercial Bank.
Standard Chartered nominees a/c ke11450 (anonymous) has shares in two banks, Housing Finance and Barclays Bank of Kenya
******
Stanbic Bank Kenya Limited (SBK) was established in 1958 when Ottoman Bank incorporated its first subsidiary in the region. In 1969, Ottoman Bank sold its Kenyan operations to National and Grindlays Bank (NGB Kenya) making its exit from the East African market. Stanbic nominees ltd a/c nr00901 is the top shareholder at Stanbic bank with 60.0% shares, followed by Standard Chartered nominees non-resd. a/c 9866 with 34 Million shares, Standard Chartered nominees non -resd. a/c 9867 with 13 Million shares, Standard Chartered Kenya nominees Ltd, a/c ke20510 with 9 Million shares, Standard Chartered Kenya nominees Ltd a/c ke002012 with 8 Million shares, Standard Chartered nominees Ltd non-resd a/cke11663 with 7 Million shares, Standard Chartered nominees non-resd. a/c ke9053 with 5 Million shares, the Permanent Secretary to the Treasury of Kenya with 4.3 Million shares, Standard Chartered nominee account ke17661 with 4.1 Million shares and Standard Chartered Kenya nominees ltd a/c ke23050 with 3.6 Million shares.
******
Diamond Trust Bank Group is an African banking group active in Burundi, Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda. It has operated in East Africa for over 70 years. It is an affiliate of the Aga Khan Development Network (AKDN) and the flagship of DTB Group is Diamond Trust Bank (Kenya), which was founded in 1946. Aga Khan Fund for Economic Development is the top shareholder at Diamond Trust Bank with 16.5% shares, followed by Habib Bank Limited with 45 Million shares, The Jubilee Insurance Company of Kenya Limited with 27 Million shares, Standard Chartered Nominees a/c KE18965 and ,Standard Chartered Nominees a/c KE18972 have 5.2 Million shares, The Diamond Jubilee Investment Trust (U) Limited with 3.8 Million shares, Standard Chartered Nominees a/c KE002382 with 3.5 Million shares, Aunali Fidahussein Rajabali and Sajjad Fidahussein Rajabali with 3.3 Million shares, Standard Chartered Nominee Non Resd a/c KE11752 and CFC Stanbic Nominee Limited a/c NR1873738 have with 2.7 Million shares.
******
Housing Finance Limited is a large mortgage finance company in Kenya. The company was established in November 1965, to promote a savings culture and homeownership among the citizens of newly independent Kenya. Major investors in the company include the Commonwealth Development Corporation (CDC), whose shareholding at one time was as high as 60%, and the Government of Kenya, which at one time owned 50% of the company. CDC has since divested from Housing Finance Limited and the Kenyan Government has substantially reduced its shareholding.
In 1992 Housing Finance Company of Kenya became listed on the Nairobi Stock Exchange.
Britam Investment Company (Kenya) Ltd is the top shareholder at Housing Finance with 19.9% shares, followed by Equity Nominees Limited a/c 00104 with 44 Million shares, Britam Insurance Company (Kenya) Ltd with 33 Million shares, Britam Insurance Company (Kenya) Ltd with 23 Million shares,Standard Chartered Nominees Resd a/c KE 11401 with 14 Million shares, SCB a/c Pan African Unit Linked FD with 11 Million shares,Permanent Secretary Treasury with 8 Million shares,Kenya Commercial Bank Nominees Ltd a/c 915B with 5 Million shares,Standard Chartered Nominees Resd a/c KE11450 and Kenya Commercial Bank Nominees Ltd a/c 915A have 4 Million shares.
*******
Investments & Mortgages Limited was formed as a private company providing personalised financial services to business people in the Nairobi area. In 1980, I&M, as the company was known at that time, was registered as a Financial Institution under the Banking Act. Following changes in the regulations of the Central Bank of Kenya, I&M became a commercial bank in 1996. In 2013, I&M Bank created I&M Holdings Limited, as the holding company of all the group’s businesses and subsidiaries. The holding company’s shares of stock are listed and publicly traded on the Nairobi Securities Exchange under the symbol I&M. Minard Holdings Limited is the top shareholder at I&M Holdings with 19.9% shares, followed by Tecoma Limited with 76 Million shares, Ziyungi Limited with 73 Million shares, Standard Chartered Kenya nominees Ltd a/c ke002796 with 41 Million shares.
********
Kenya Reinsurance Corporation has shares in two banks, Cooperative Bank and National Bank of Kenya.
******
National Social Security Fund (NSSF) has shares in two banks, National Bank of Kenya and Kenya Commercial Bank.
******
NIC Custodial Services a/c 077 (anonymous) has shares in two banks, Cooperative Bank of Kenya and National Bank of Kenya.
******
The National Treasury has shares in two banks, Kenya Commercial Bank and National Bank of Kenya.
*****
The Jubilee Insurance Company of Kenya Limited has shares in two banks, Diamond Trust Bank and Barclays Bank of Kenya.
********
Banks play an important role in the economy of a country. When banks efficiently mobilize and allocate funds, this lowers the cost of capital to firms, boosts capital formation, and stimulates economic activities. Thus, weak governance in the banking sector can have far-reaching consequences to the economy of a country. In the recent past, the banking sector in Kenya has witnessed a number of corporate governance issues that sent jitters among millions of bank customers resulting in a confidence crisis. While banks have begun to adhere to disclosure requirements spelt out in the prudential guidelines issued by the Central Bank of Kenya (CBK) much more needs to be done, particularly pertaining to competition policy and regulation to put checks and balances on the monopolisation of the banking sector in Kenya.
This story was produced in partnership with Code for Africa’s iLAB data journalism programme, with support from Deutsche Welle Akademie.